Drupal CMS Installation on Ubuntu Linux with Apache Support: A Step-by-Step Guide

The Drupal content management system (CMS), built on PHP, is designed to empower enterprises and business owners by enabling seamless collaboration and automating the creation of engaging customer experiences at every stage of the process.
A step-by-step guide on installing Drupal on Ubuntu Linux with Apache web server support.
A step-by-step guide to installing and configuring Apache2 for your Drupal site.
Drupal CMS relies on a web server to function, and Apache2 is one of the most widely used options today. To set up Apache on Ubuntu, simply run the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install apache2
Use the following commands to stop, start, and enable the Apache2 service, ensuring it automatically starts whenever the server boots.
sudo systemctl stop apache2.service
sudo systemctl start apache2.service
sudo systemctl enable apache2.service
To ensure everything went smoothly, perform a quick check by opening your server’s public IP address in a web browser.
http://your_server_ip
The default Apache web page on Ubuntu 22.04 serves as a resource for information and testing. Below is an example of the default Apache web page:
Guide to Installing MySQL for Your Drupal Website
To store and manage your site’s data, you need to install a database system. MySQL, a widely used database management system, is particularly popular in PHP environments.
Drupal also requires a database server, and MySQL is an excellent choice for those seeking an open-source database solution.
To install Drupal, simply execute the following commands.
sudo apt install mysql-server
confirm installation by typing Y, and then ENTER.
Once the installation is complete, make sure to run the security script that comes pre-installed with MySQL.
Start by opening the MySQL prompt:
sudo mysql
Next, execute the following command:
ALTER USER command to change the root user’s authentication method to one that uses a password. The following example changes the authentication method to mysql_native_password:
ALTER USER ‘root’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY ‘password’;
Once you have made this change, exit the MySQL prompt:
mysql> exit
Begin the interactive script by executing the following command:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
This will prompt you to configure the… VALIDATE PASSWORD PLUGIN.
Answer Y for yes, or anything else to continue without enabling.
VALIDATE PASSWORD PLUGIN can be used to test passwords
and improve security. It checks the strength of password
and allows the users to set only those passwords which are
secure enough. Would you like to setupVALIDATE PASSWORDplugin?Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No:
If you answer “yes”, you’ll be asked to select a level of password validation. Keep in mind that if you enter 2 for the strongest level, you will receive errors when attempting to set any password which does not contain numbers, upper and lowercase letters, and special characters:
There are three levels of password validation policy:
LOW Length >= 8
MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters
STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file
Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG: 1
Regardless of whether you chose to set up the VALIDATE PASSWORD PLUGIN , your server will next ask you to select and confirm a password for the MySQL root user. This is not to be confused with the system root. The database root user is an administrative user with full privileges over the database system. Even though the default authentication method for the MySQL root user doesn’t involve using a password, even when one is set, you should define a strong password here as an additional safety measure.
If you enabled password validation, you’ll be shown the password strength for the root password you just entered and your server will ask if you want to continue with that password. If you are happy with your current password, enter Y for “yes” at the prompt:
Estimated strength of the password: 100
Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : y
For the rest of the questions, press Y and hit the ENTER key at each prompt. This will remove some anonymous users and the test database, disable remote root logins, and load these new rules so that MySQL immediately respects the changes you have made.
Once you’ve completed the setup, verify your access to the MySQL console by typing the following command:
sudo mysql
This will connect to the MySQL server as the administrative database user root, which is inferred by the use of sudo when running this command. Below is an example output:
Output :
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 10
Server version: 8.0.28-0ubuntu4 (Ubuntu)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Type ‘help;’ or ‘\h’ for help. Type ‘\c’ to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
exit the MySQL
mysql> exit
Install PHP
PHP is a key component of our setup, responsible for processing code and delivering dynamic content to users in real time.
For the PHP package, you’ll need the php-mysql module, which enables PHP to interact with MySQL-based databases.
sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-php php-mysql
After the installation is complete, execute the following command to verify your PHP version:
php -v
PHP 8.1.2 (cli) (built: Mar 4 2022 18:13:46) (NTS) Copyright (c) The PHP Group Zend Engine v4.1.2, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v8.1.2, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
Then update and upgrade to PHP 7.*
sudo apt update
Install PHP 7.x or 8.x along with the necessary additional packages..
Check PHP version and replace with * sign.
sudo apt-get install php7.*-cli php7.*-common php7.*-json php7.*-opcache php7.*-mysql php7.*-xmlrpc php7.*-mbstring php7.*-gd php7.*-zip php7.*-fpm php7.*-intl php7.*-simplexml php7.*-mcrypt php7.*-soap php7.*-curl
Execute the following commands to open the default Apache2 PHP configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/php/7.1/apache2/php.ini
Then change to the following lines below in the file and save.
file_uploads = On
allow_url_fopen = On
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 64M
max_execution_time = 30
display_errors = Off
max_input_vars = 1500
date.timezone = America/Chicago
Guide to Installing Drupal CMS: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
How to Create a Drupal Database: A Step-by-Step Guide
Log in to the MySQL shell. When prompted for a password, simply press ENTER to continue.
sudo mysql -u root -p
Set up a MySQL database named 'drupal' for your Drupal installation.
CREATE DATABASE drupal10;
Create a database user named 'drupal' and assign a secure password to it.
CREATE USER ‘drupal’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘StrongPassword’;
Provide the user with full administrative access to the database.
GRANT ALL ON drupal.* TO ‘drupal’@’localhost’ WITH GRANT OPTION;
Don’t forget to save your changes.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Exit the shell and return to the main environment.
EXIT;
Unzip or extract the contents of the archive.
sudo unzip drupal-10.1.4.zip
Set up the installation directory
/var/www/html/.
sudo mkdir /var/www/html/
Transfer ownership of the installation directory.
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/
Update the access permissions for the directory.
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/
How to Configure Apache2 for Optimal Performance with Drupal
Create an Apache Virtual Host configuration file for Drupal.
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/drupal.conf
Insert the following code into the file, then save and close it.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@example.com
ServerName example.com
ServerAlias www.example.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/
Options +FollowSymlinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/drupal_error.log
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/drupal_access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Verify that the file syntax is properly formatted.
sudo apachectl -t
Update the Apache configuration directory.
cd /etc/apache2/sites-available/
Disable the default Apache configuration file to enhance security and optimize performance.
sudo a2dissite 000-default.conf
Activate the Apache configuration file for Drupal CMS.
sudo a2ensite drupalcms.conf
Activate Apache Rewrite Module.
sudo a2enmod rewrite
To ensure the changes are applied, restart the Apache service.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Enhancing the User Experience with the Drupal CMS Web Interface
To access the Drupal CMS web interface, open your browser and navigate to http://Server_IP/. For example:
http://192.168.1.31/Drupal
Next, simply follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation of Drupal successfully.
Visit the Drupal 10.1.4 page, select your preferred language, and click to proceed. Save and continue button.
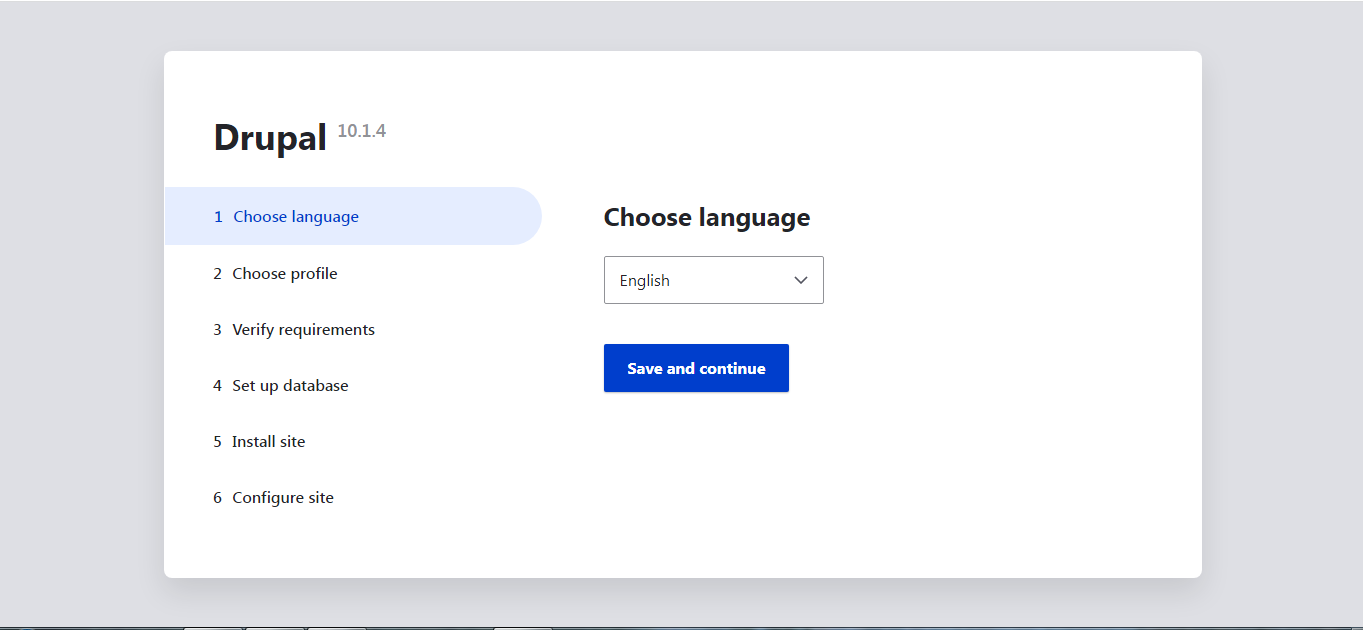
Navigate to the Installation Profile section, select an option from the ‘Select an Installation Profile’ dropdown menu, and click on the desired profile Save and continue.
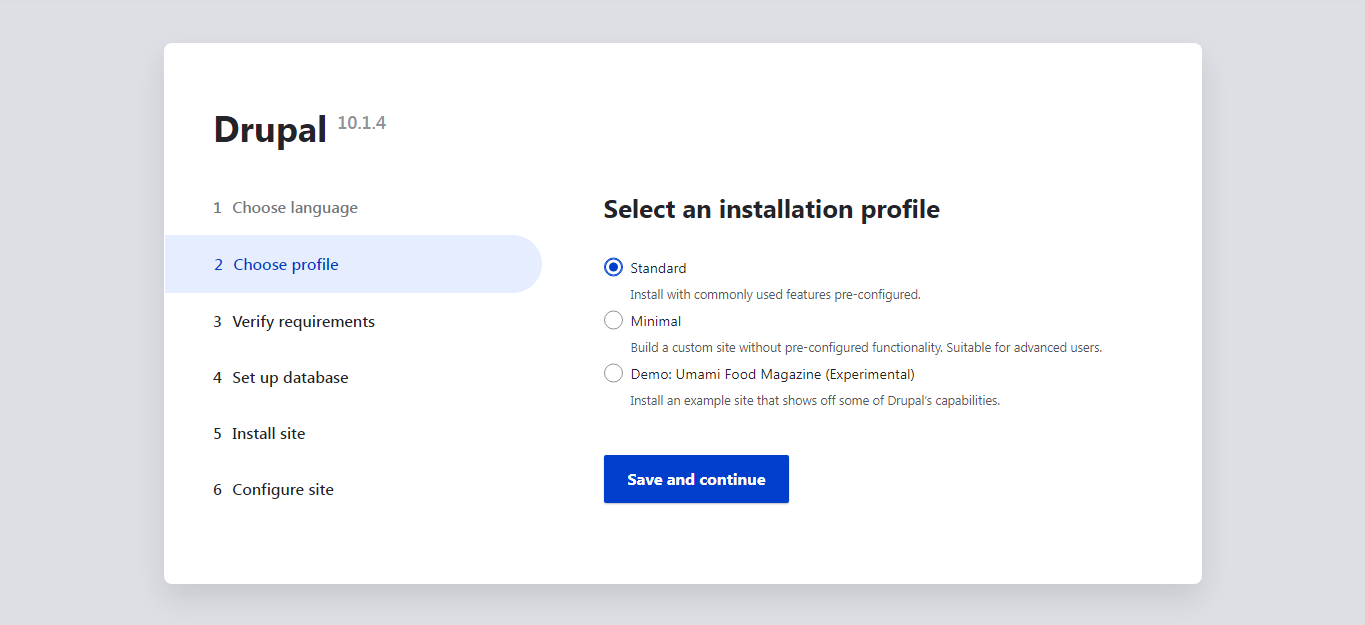
Review the requirements and ensure that all necessary information is provided as outlined below.
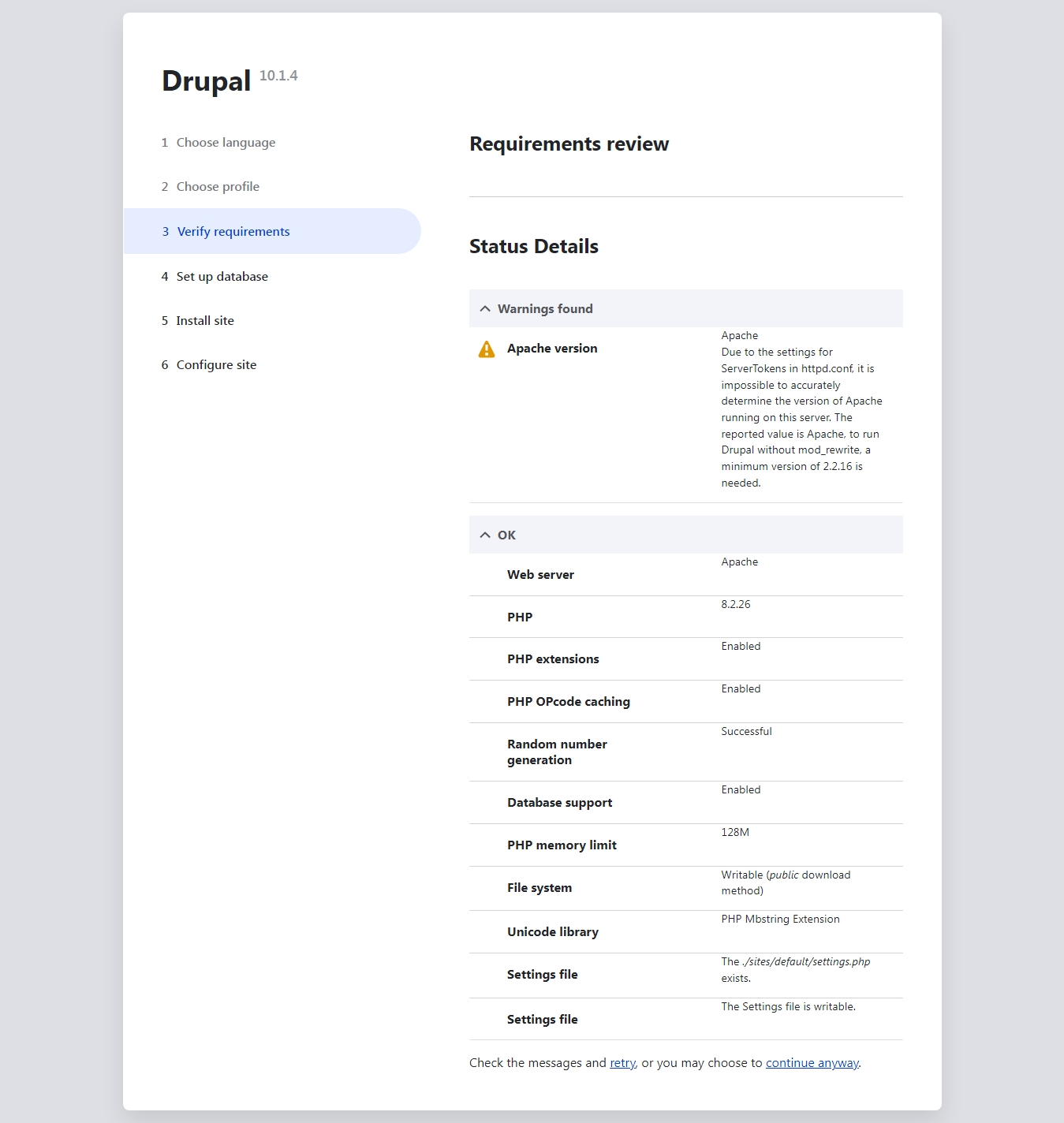
Review the requirements and click on the button to proceed continue anyway.
Configure and Set Up the Database for Optimal Performance
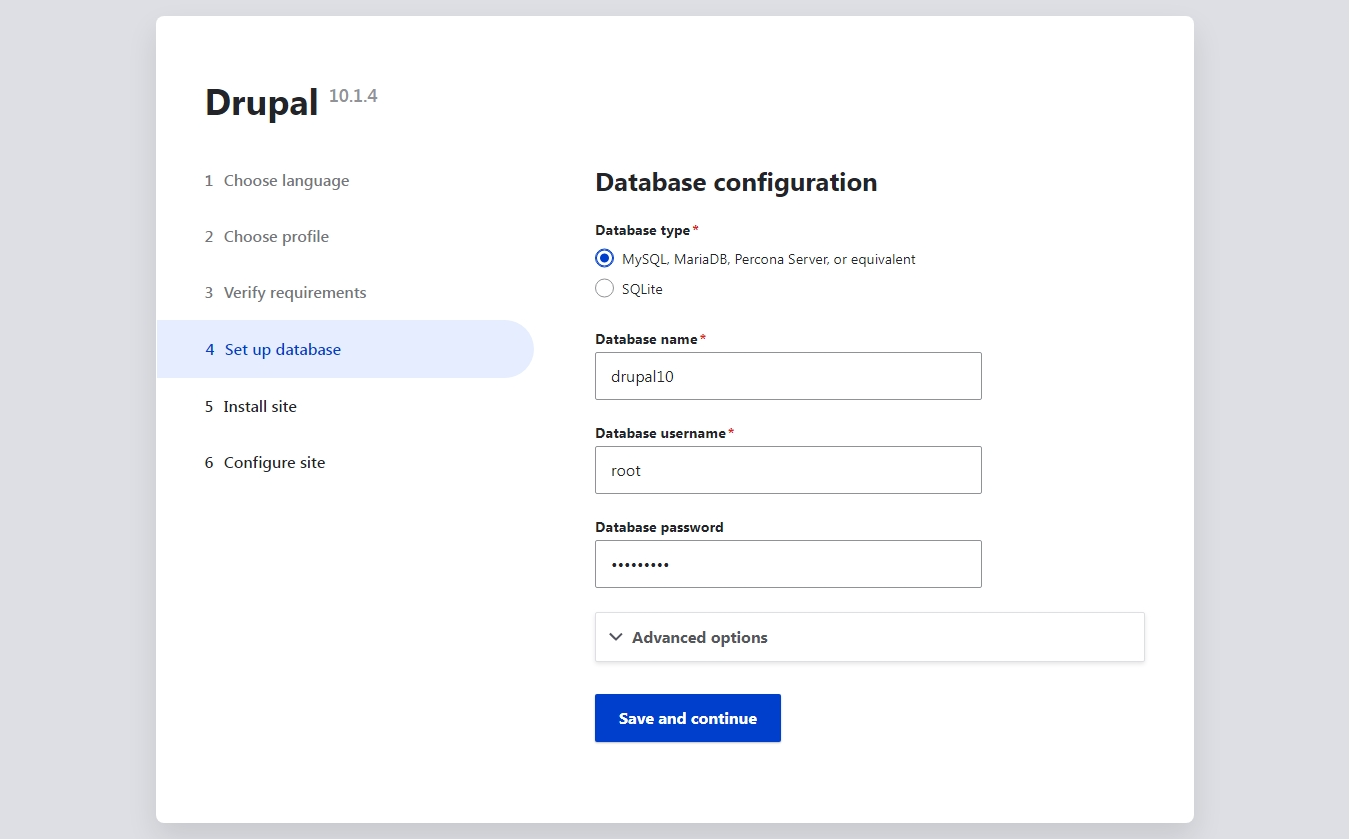
Complete all the required fields and click on the Save and continue to proceed.
Install Site
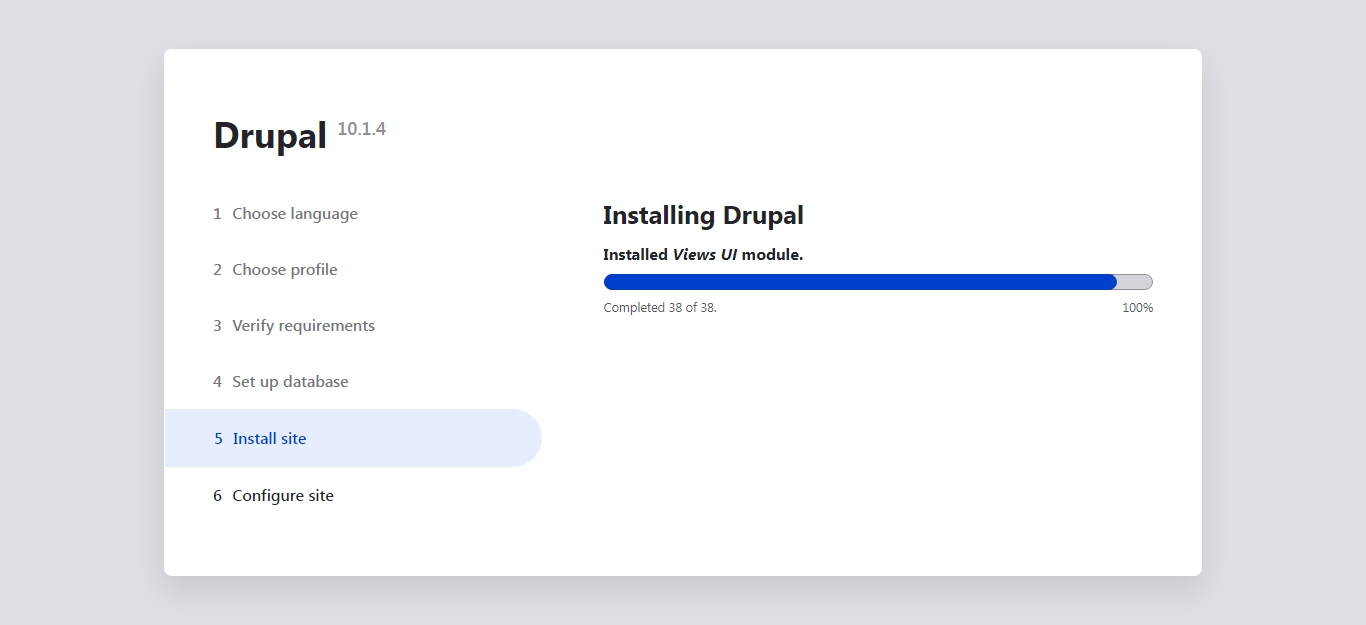
Complete the installation of your Drupal site.
Configure Site

Complete all the required fields and click on the Save and continue to proceed.
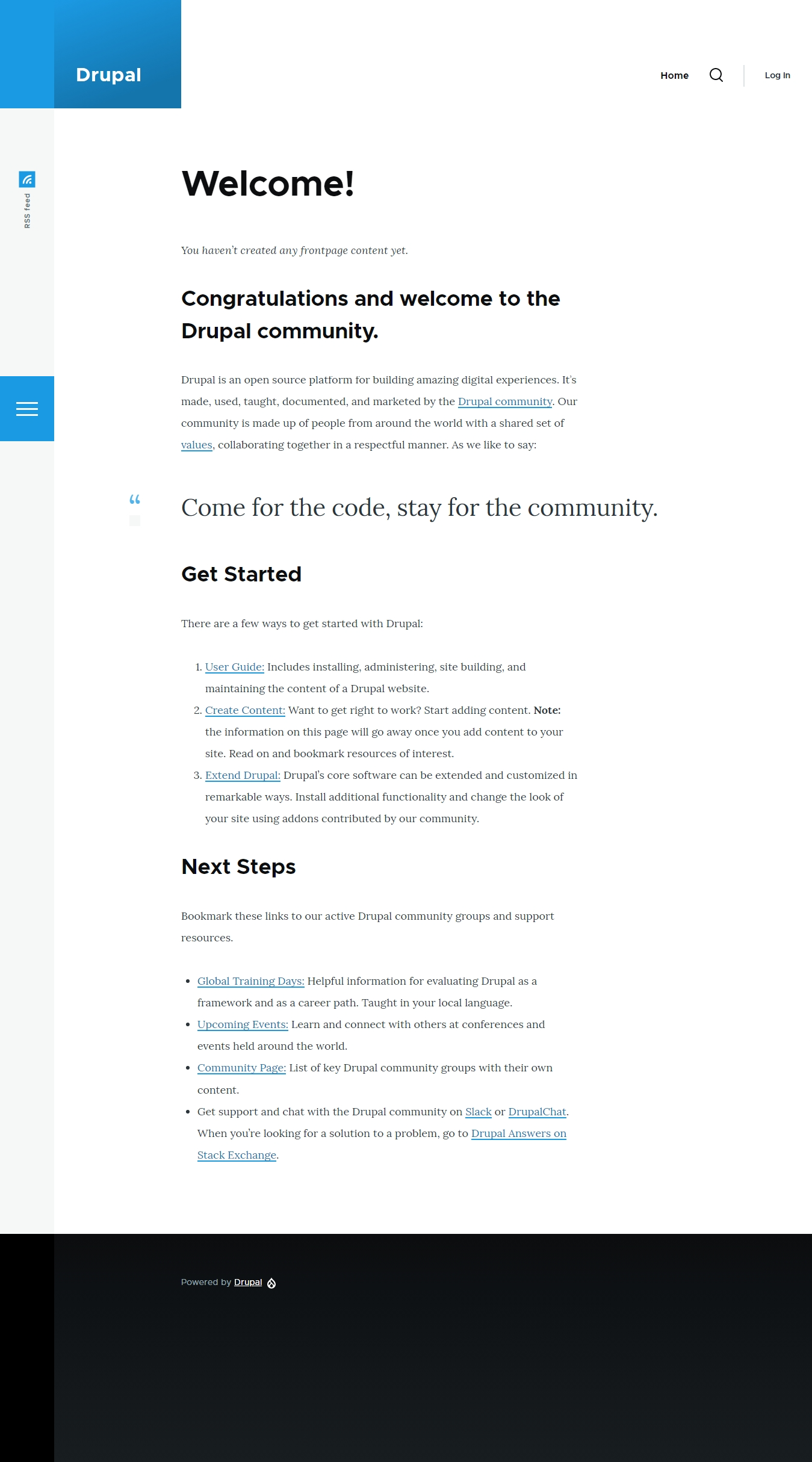
After a short period, the installation will be complete, and the platform will be ready for use.
Enjoy!